Algorithms determine who we interact with in our newsfeeds. The rank websites in the world's biggest search engine. They teach robots to learn, and to imagine. They even automate stock market trading. In many ways, algorithms have made software developers the rulers of the modern world. But what are they exactly? Where did they come from? And how will they program our future?
Algorithm: A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other program - solving operations, especially by a computer.
ORIGIN OF THE ALGORITHM
The term "algorithm" was derived from Al-Khwarizmi (c. 780-850), a Persian mathematician, astronomer, geographer, and scholar. The first recorded mathematical algorithms date back to 1600 BC, when Babylonians developed the for the purposes of factorization and finding square roots.
Modern algorithms took shape in the late 1920s, and were formalized throughout the 1930s with the introduction of recursive functions by Gödel-Herbrand-Kleene, lambda calculus by Alonzo Church, formulations by Emil Post, and Turning machines by Alan Turning.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN ALGORITHM
1. It must stop at a certain point.
If the task is to ate a cake, the algorithm is a cake recipe where you are instructed on what to prepare, what to mix, what oven temperature to set, and when to stop baking to produce a perfectly made cake.
2. It must have well-defined instructions with specific steps.
If the task is to locate the park, the algorithm is a set of directions which will clearly explain what to do and where to go to reach the park.
3. It must be effective in solving the problem it was designed to solve.
If the task is to build a toy plane, the algorithm is an instruction manual which will guide you on which parts to put together to end up with a fully-assembled toy.
DOMINANT ALOGRITHMS
Link Analysis
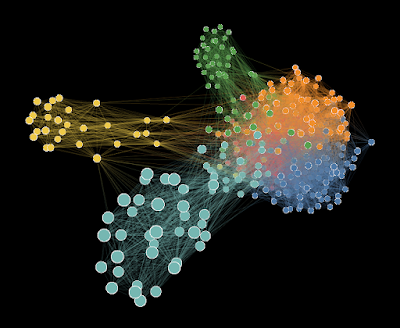
From search engines, social networks to online marketing, the analysis of relationships between various entities is paramount. There are many approaches and characteristics of link analysis and each can be an algorithm, although the bases are similar. Think about Google's PageRank, Facebook's friends suggestion, YouTube's recommended videos or Netflix movies - the parameters may be different but the math behind them is essentially the same.
Link analysis is a data-analysis technique used in network theory to evaluate node relationships (connections). Relationships can be identified between various types of nodes (objects), such as organizations, people, and transactions. Link analysis has been used in the investigation of criminal activity (fraud detection, counterterrorism, and intelligence), computer security analysis, search engine optimization, market research, medical research, and art.
Data Compression
From zip to mp3 and from JPEG to MPEG-2, these algorithms compress data to make systems cheaper, more efficient and easier to transmit. Data compression is used in video games, videos, music, cloud computing, data storage, databases, and anything you download in your computer, just to name a few examples.
Data compression refers to the process of reducing the size of a data file. Source coding refers to encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted in the context of data transmission.
RSA
Developed by the founders of the RSA company, this algorithm introduced cryptography and made it available for everyone. The algorithm solved a simple but complex problem - how to share public keys between final users and independent platforms. The RSA algorithm is applied for both public key encryption and digital signatures, and is widely used fir securing sensitive data sent over an insecure network such as the internet.
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a popular public-key cryptosystem for secure data transmission. It is also among the oldest. The abbreviation "RSA" is derived from the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, who published the algorithm in 1977. Clifford Cocks, an English mathematician, developed an equivalent system in secret at Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), the British signals intelligence agency, in 1973. In 1997, that system was declassified.
Secure Hash
This is a family of cryptographic hash functions developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology. The resulting hash from these algorithms verifies that the file you receive is the correct one by comparing its hash with the internet elements use these hash algorithms to check that what you download is not the result of some phishing or online attack.
Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA) are a type of cryptographic function that is used to keep data secure. It transforms data using a hash function, which is an algorithm composed of bitwise operations, modular additions, and compression functions. The hash function then returns a fixed-length string that bears no resemblance to the original. These algorithms are designed to be one-way functions, which means that once they've been transformed into their respective hash values, it's nearly impossible to reverse the process.
Merge Sort, Quick Sort and Heap Sort
The comparison-based sorting algorithm Merge Sort uses a "divide and conquer" algorithm just like Quick Sort although the latter has a different sorting approach, is less stable and more suited for RAM-based arrays. On the other hand, the Heap Sort algorithm uses a priority are some of the most important ones used in data mining, artificial intelligence, link analysis and most computing operations.
A Sorting Algorithm is used to rearrange elements in an array or list based on a comparison operator on the elements. The comparison operator determines the new order of elements in a data structure.
Proportional Integral Derivative
You can see this algorithm in action everywhere-vehicles, airplanes, cell phone network, satellite service, factories, and even robots. It is a control loop feedback mechanism to reduce the error between desired output signal and real output signal. It is applied anywhere there is a need for signal processing or an electronic system controlling a mechanical, hydraulic or thermal system using automation.
A proportional-integral-derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a feedback-based control loop mechanism that is widely used in industrial control systems and other applications that require continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value e(t)e(t) as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D, respectively), thus the name.
Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Algorithms
These two algorithms convert signals from their time domain into their frequency domain and vice versa. The internet, modems, smartphones, tablets satellites, laptops - essentially, everything in the digital world or anything with a computer in it uses these algorithms.
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes a sequence's discrete Fourier transform (DFT) or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis transforms a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a frequency domain representation and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into frequency components. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is frequently too slow.
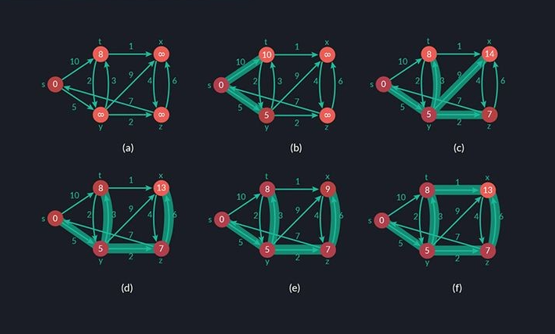
Dijkstra's Algorithm
This search algorithm can be modeled as graph in order to enable giving the shortest path between tow nodes. although there other methods to finding the shortest path, Dijkstra's algorithm is preferred for systems that need stability. A variant of this algorithm applied today in the field of artificial intelligence.
Dijkstra's algorithm is a method for determining the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which could represent a road network. Edsger W. Dijkstra, a computer scientist, devised it in 1956 and published it three years later.
Integer Factorization
A mathematical algorithm which is a series of steps used to get the prime factorization of a composite number into smaller non-trivial divisors. this is heavily used in the computing field, particularly in cryptography where protocols are based on the difficulty of factoring large composite integer.
In number theory, integer factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number into smaller non-trivial divisors that, when multiplied together, equal the original integer.
Algorithms will have many useful applications in occupational safety and health in the future. While algorithm-enabled systems and devices may reduce human error and improve worker safety and health, algorithms may also introduce new risks to worker well-being. Determining whether an algorithm is safe for use in a worker management system, advanced sensor technologies, robotic devices, and other workplace systems, tools, and machinery will put algorithm designers and software programmers, algorithm-enabled equipment manufacturers, employers, workers, and occupational safety and health practitioners to the test.
You May Also Like:
Fingerprint Scanners - How It Works
VPN - How It Works
QR Code - How It Works
Torrent - How It Works